


Types Of Arterial Thrombus (Thrombi) and Venous Thrombus ...
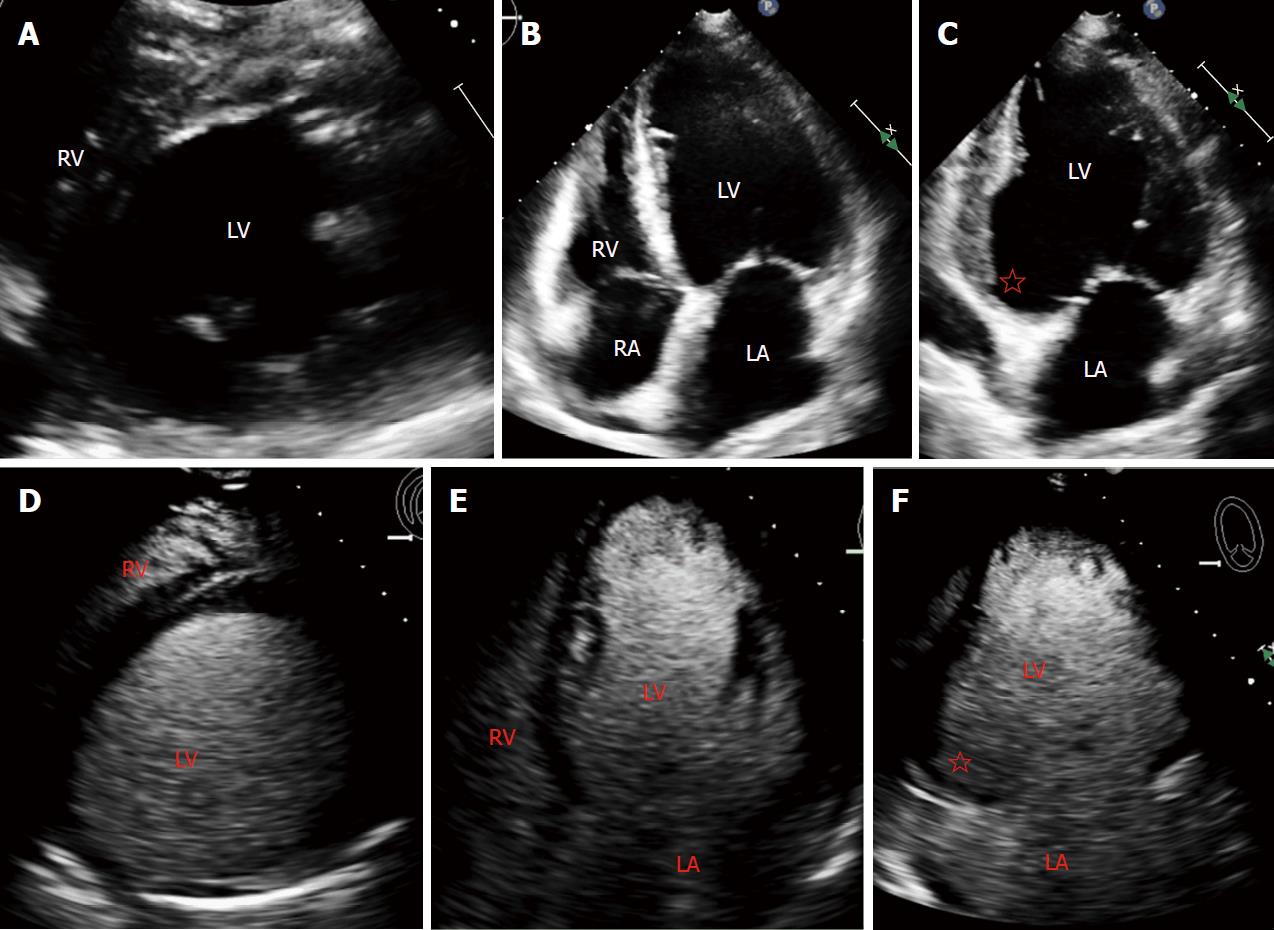
Types Of Arterial Thrombi (Thrombus) Mural Thrombus: It refers to " a thrombus that is attached to the wall of blood vessel or heart but doesn't occlude the vessel completely Sites Of Mural Thrombosis: Capacious chambers of heart, Aorta, Aneurysms.An LV apical mural thrombus was also noted. Despite sustained ventricular tachycardia and need for inotropic dose escalation due to cardiogenic shock, endomyocardial biopsy was postponed considering the risk of LV thrombus embolization.
Superiority of Echocardiography over Angiocardiography in ...
Figure 3 Post-mortem photograph of longitudinally sectioned heart Cardiac base is to right and apex to left There is an extensive, thin-walled apical left ventricular aneurysm with a large mural thrombus within the aneurysm. T is thrombus, and LV, left ventricle.Embolization of Left Ventricular Apical Thrombus During ...
The incidence of new-onset LV apical thrombus is greatest in those experiencing large anterior wall myocardial infarction with resultant apical akinesis or dyskinesis. The incidence of systemic embolization has been reported to be as high as 10%. 1 Manipulation of the heart during cardiac surgery has the potential to further increase this risk.Case Report Open Access Left Ventricular Mural Thrombus ...
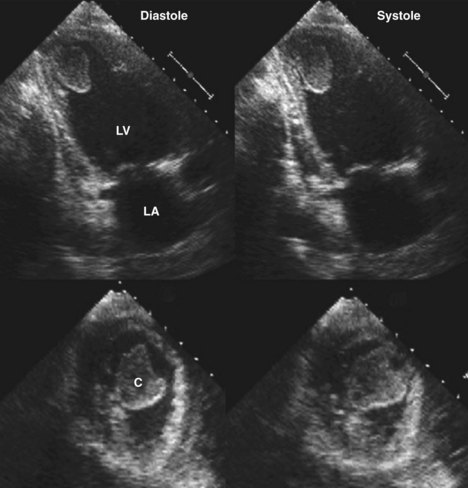
(Figure 2). Left ventriculography demonstrated antero-apical lv apical mural thrombus akinesia, and a 1.4 x 1.0 cm apical mural thrombus. The mural thrombus was confirmed by echocardiography (Figure 3). Figure 3: Two dimensional echocardiogram showing left ventricular antero-apical akinesia and the apical mural thrombus (large arrow), whichdetection of mural thrombus. Echocardiography is also widely available and lv apical mural thrombus relatively inexpensive. It is now the method of choice for detecting left ventricular thrombus, although the sensitivity oftwo-dimensional echocardio-graphyin the detectionofleft ventricular thrombusvaries between77and95%
Improved Detection by Delayed-Enhancement CMR of LV ...
Mural thrombus formation on an infarcted segment of the left ventricle (LV) is a well-recognized complication of a myocardial infarction (MI). A majority of these thrombi occur within the first 30 days after an anterior ST-segment elevation lv apical mural thrombus myocardial infarction (STEMI) and are considered a cause of embolic strokes during the post-MI period.Case report Off label use of direct oral anticoagulants ...
sensitivity (95%) in detecting LV thrombus in Figure 1. A. This is an apical view of the left atrium and left ventricle and the presence of a left ventricular thrombus in the apex. B.This is an enlarged apical view of the left ventricle again demonstrating the left ventricular api-cal thrombus.Dec 04, 2018 · The international normalized ratio (INR) recommendations below are per guidelines from the American College of Chest Physicians (2008). Rheumatic mitral valve disease INR target (range) Atrial fibrillation (AF), prior embolism, and/or left atrial thrombus: 2.
RECENT POSTS:
- louis vuitton smiley flower bags
- lv damier ebene eva clutch
- harga tas louis vuitton monogram
- amazon ladies bags below 200
- lv noe purse minimum
- where to buy designer bags in canada
- vest for sale online
- supreme and louis vuitton shorts
- authentic bag for sale philippines
- louis vuitton dauphine bag
- iphone 8 plus sale in lahore
- louis vuitton bags outlet orlando florida
- louis vuitton shoes price list south africa
- speedmaster speedy tuesday

Share your thoughts