


Recurrent Left Ventricular Thrombus Formation on ...
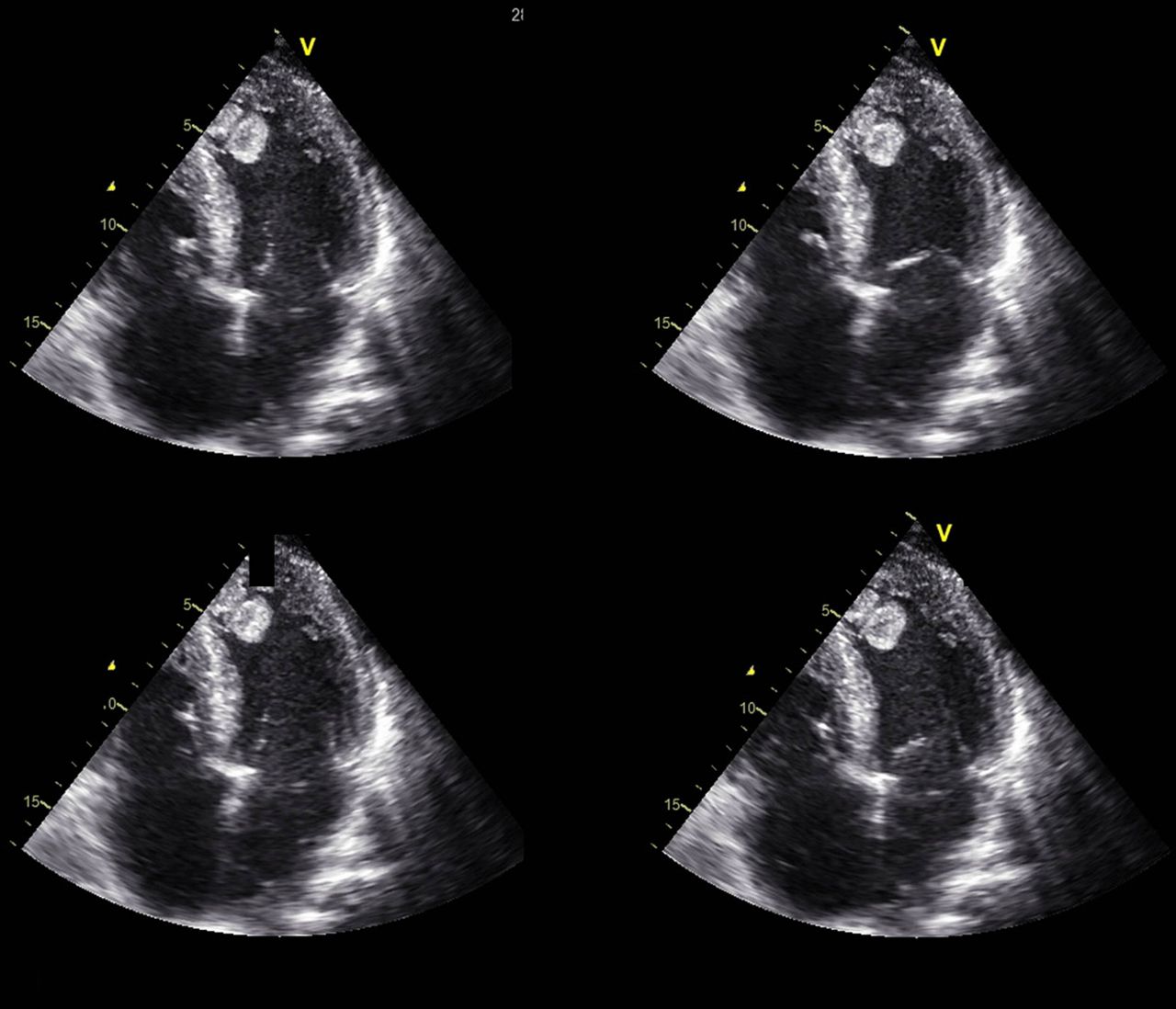
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus in patients with reduced LV systolic function carries significant thromboembolic risk. Direct oral anticoagulants are an attractive alternative to warfarin for LV thrombus management. However, there are not enough data regarding the safety and efficacy of direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of LV thrombus.The left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction was esti-mated at 30%–35% with a dyskinetic apex, inferior wall hypokinesia, anterolateral wall akinesia, grade one LV diastolic dysfunction and central mitral regur-gitation (1+). A 2.5 cm × 1.2 cm apical, protruding, but relatively immobile, left ventricular thrombus (LVT) was detected (Fig. 1).
LV thrombus was associated with apical LV dysfunction Bière 2016 [14] 329 STEMI (183 anterior) Single centre Age: 58±11 years Male: 82% DM: 12% Smoker: 43% MI size: 20±13% 1.5 T and 3 T Day 6 (4 – 8) and at 3 months First pass perfusion 22 (6.7%) early LV thrombus and 9 (2.9%) late LV thrombus All LV thrombus were in anterior STEMI
Sep 19, 2010 · LV thrombus was detected in 30 (42.8%) patients. ACA IgM levels were significantly higher in the patient group with LV thrombus than in the group without thrombus (12.44 ±4.12 vs. 7.69 ± 4.25 mpl, p = 0,01). ACA IgG levels were also found higher in the group with LV thrombus (24.2 ± 7.5 vs.17.98 ± 6.45 apical lv thrombus gpl, p = 0.02).
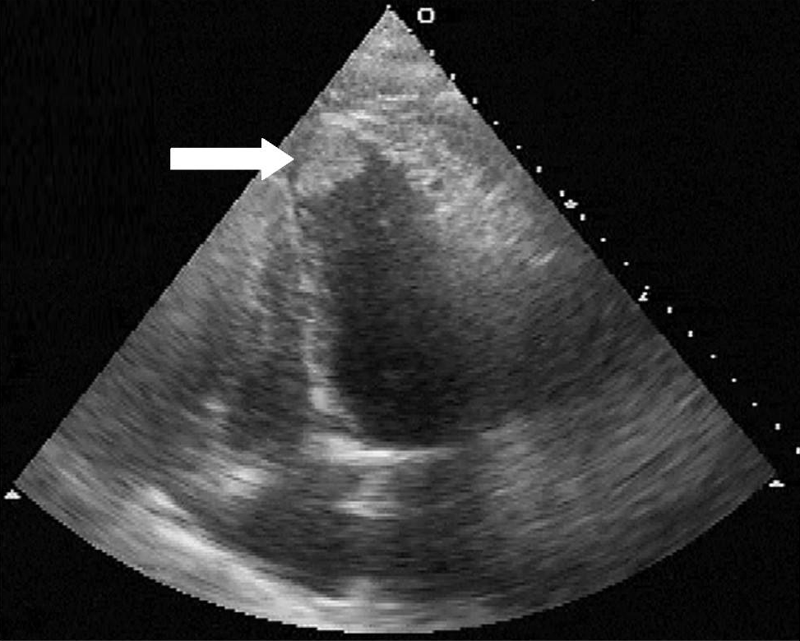
An LV thrombus is defined as a discrete echodense mass in the LV with defined margins that are distinct from the endocardium and is seen throughout systole and diastole It is located adjacent to an area of the LV wall which is hypokinetic or akinetic and seen in 2 views (usually apical and short axis)
Mid cavity hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy with ...
Moreover, the presence of apical wall motion abnormality, following an anterior or inferior infarction, compared to its absence has proven to be associated with high risk for Left Ventricular (LV) thrombus formation even in patients without HOCM .Left Ventricular Thrombus or Myxoma: The Use of ...
There have been several case reports of thrombus mimicking cardiac tumors. Left ventricular apical lv thrombus thrombus formation is a well-known complication of a myocardial infarction, LV aneurysm, cardiomyopathy or a hypercoagulable state. It is uncommon for a thrombus to form in a normal LV in the absence of a wall motion abnormality.Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with apical akinesia and lv ...
Echocardiography showed LV apical thinning and akinesia with mid cavity hypertrophy and a possible mass in the apex suggestive of thrombus. Blood results showed normal full blood count, electrolytes and renal function but a raised troponin level. louis vuitton outletCureus | Right Atrial Thrombus in a Patient With COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a worldwide pandemic. Evidence suggests a strong association between COVID-19 and pro-thrombotic states. We report our experience in managing a patient with COVID-19 complicated by a right atrial thrombus. We highlight the successful use of half-dose anticoagulation in the treatment of right atrial thrombus in a patient with COVID-19.RECENT POSTS:
- lv multiple wallet damier graphite
- lv flower zipped tote
- mt st louis lift passenger
- sell designer bags houston tx
- lv artsy mm price euro
- louis vuitton brown purse price
- 75 inch tv black friday best buy
- multi pochette accessoires lv price
- st. louis historical newspapers online
- louis vuitton jobs paris
- louis vuitton flower hobo reviews
- calvin klein dresses at macy's on sale
- mini dauphine lv bag
- louis vuitton christmas wallet 2018

Share your thoughts